Key Summary on Market Structures Economics tutor2u The perfectly competitive market structure is a theoretical or ideal model, but some actual markets do approximate the model fairly closely. Examples include farm products markets, the stock market, and the foreign exchange market. The Perfectly Competitive Firm as a Price Taker For model-building purposes, suppose a firm operates in a market
Market Structure Meaning Characteristics and Forms
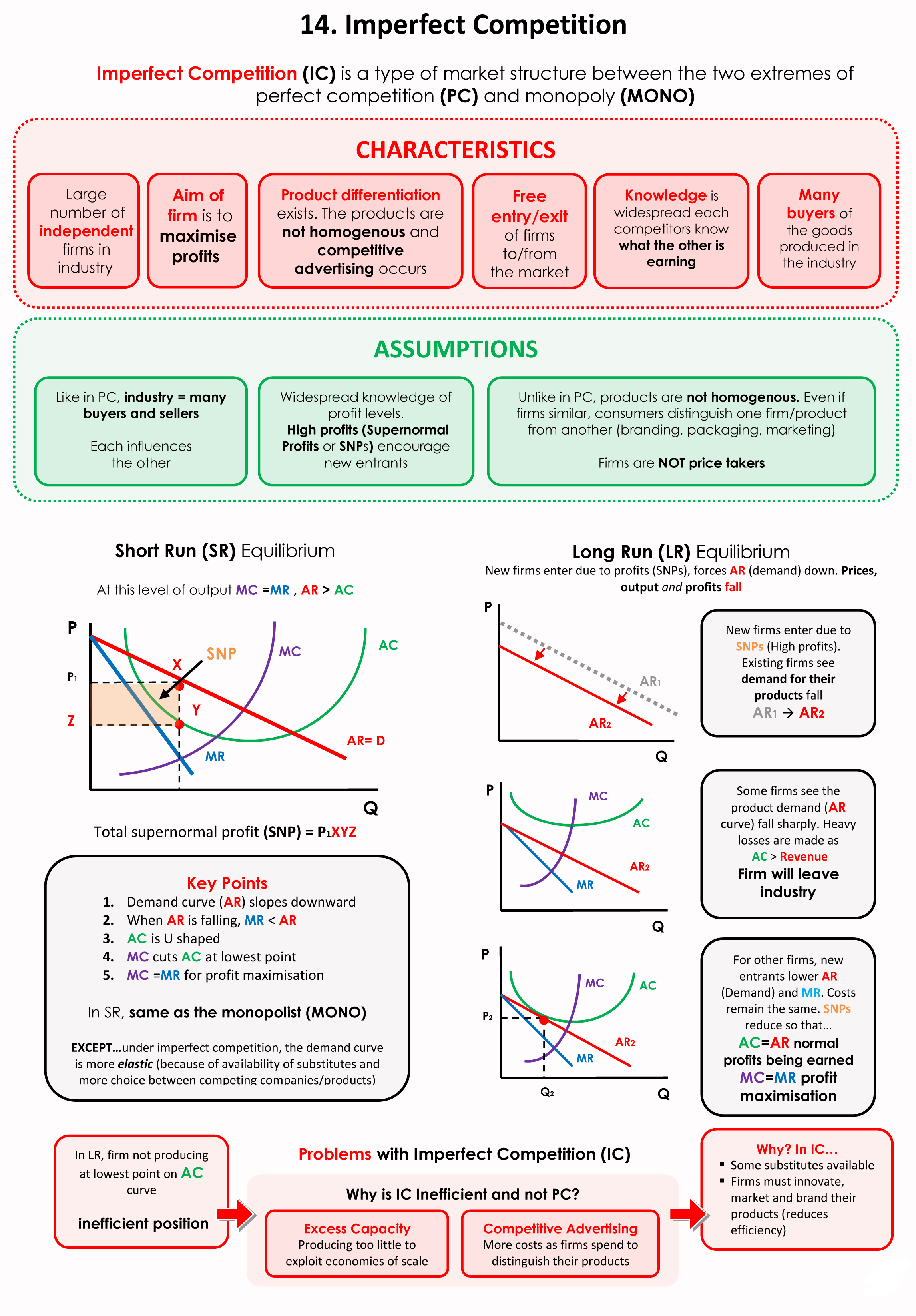
Monopoly Market Structure YouTube. Sep 21, 2017В В· Description of Monopoly Market Structure ( Written in Hindi, Explanation in Hindi ), market demand for monopolistic competition whereas for monopoly firm demand equals market demand. Similar to both monopoly and perfect completion, firms in monopolistic competition may decide to shut down. The decision is the same for all firms in the short-run: o If P > ATC => profit > 0 => produce o If P = ATC => profit = 0 => produce.
CHAPTER 10 IDENTIFYING MARKETS AND MARKET STRUCTURES market structure _____ b. a few firms that produce goods that are close substitutes In the DuPont case discussed in the text, the government argued that DuPont had a near monopoly position in the market for cellophane; thus, DuPont a. was broken up into smaller competitive companies CHAPTER 10 IDENTIFYING MARKETS AND MARKET STRUCTURES market structure _____ b. a few firms that produce goods that are close substitutes In the DuPont case discussed in the text, the government argued that DuPont had a near monopoly position in the market for cellophane; thus, DuPont a. was broken up into smaller competitive companies
The second market structure which this paper discusses relates to monopoly. A monopoly signifies a single seller of a product and for which there is no competition from other manufacturers. The Exxon Mobil is a fine example of a monopoly as it is the largest oil and gas majors in USA and the one of the six largest of the world. Jun 18, 2019В В· In a Monopoly Market Structure, there is only one firm prevailing in a particular industry. However, from a regulatory view, monopoly power exists when a single firm controls 25% or more of a particular market. For example, De Beers is known to have a monopoly in the diamond industry.
Different types of market structure 1. Perfect competition (many firms) 2. Monopoly (one firm), Oligopoly (a few firms) + monopolistic competition, contestable markets and collusion. Advantages of monopoly. 1. Monopoly avoids duplication and hence avoids wastage of resources. (We have to understand that duplicate and fake products are a real problem in many countries). 2. A monopoly enjoys economies of scale as it is the only supplier of product or service in the market. The benefits can be passed on to the consumers. 3.
ADVERTISEMENTS: Market structure refers to the nature and degree of competition in the market for goods and services. The structures of market both for goods market and service (factor) market are determined by the nature of competition prevailing in a particular market. Meaning of Market: Ordinarily, the term “market” refers to a particular place where […] Market structure. Insurance market structure can be defined in a number of ways. Three of the most common measures include the total number of insurers operating in the relevant geographic and product market; a four-firm concentration ratio that provides the percentage of market share captured by the largest four firms in the market; and the
market demand for monopolistic competition whereas for monopoly firm demand equals market demand. Similar to both monopoly and perfect completion, firms in monopolistic competition may decide to shut down. The decision is the same for all firms in the short-run: o If P > ATC => profit > 0 => produce o If P = ATC => profit = 0 => produce Oct 25, 2015 · As one can see from the above that monopoly has both advantages and disadvantages, however majority of the governments as well as consumers all over the world don’t prefer pure this market structure because most of the times it leads to exploitation of consumers by monopolist.
ADVERTISEMENTS: Market structure refers to the nature and degree of competition in the market for goods and services. The structures of market both for goods market and service (factor) market are determined by the nature of competition prevailing in a particular market. Meaning of Market: Ordinarily, the term “market” refers to a particular place where […] The Economics Department at CSUSB provides students an excellent liberal arts education. Students majoring in economics learn the basics of economics and receive a rigorous training in logical and empirical analysis.
Lecture 6: Market Structure – Perfect Competition I. Concepts of Competition Whether a firm can be regarded as competitive depends on several factors, the most important of which are: • The number of firms in the industry. As the number of firms increases, the effect of any one firm on the price and quantity in the market declines. Warm Up List your favorite brand for the following: Jeans Shampoo Shoes Explain why you like these particular brands? Chapter 7 Competition, Market Structures, and the Role of Government 12.2.8 the role of profit as the incentive to the entrepreneurs in a market economy Market Structures What is the primary aim/goal of businesses?
Dec 09, 2009В В· what is monopoly, its characteristics, probable cause & equilibrium price and output in short n long run. u can mail me ur views on rajeshkr.1128@gmail.com Dec 09, 2009В В· what is monopoly, its characteristics, probable cause & equilibrium price and output in short n long run. u can mail me ur views on rajeshkr.1128@gmail.com
Monopoly vs. Competitive Market. Monopolies and competitive markets mark the extremes in regards to market structure. There are a few similarities between the two including: the cost functions are the same, both minimize cost and maximize profit, the shutdown decisions are the same, and both are assumed to have perfectly competitive market factors. Monopolistic Competition Market structure that combines monopoly and competition— Monopolistic Competition. – Where there are many buyers buying slightly different products. – Where there are just a few sellers. Examples of these types of markets are – Automobiles – Soft drinks – Hotels/restaurants. 52
Get help on гЂђ Market Structures: Monopoly, Monopsony, Oligopoly, Monopolistic Competition Essay гЂ‘ on Graduateway Huge assortment of FREE essays & assignments The best writers! Market structure by Ilya Malyavin (14840019) In some cases monopoly may occur from the oligopoly. It happened when key companies arrange to act together as a monopoly (Parkin, 2008). However such collusive agreements are illegal in New Zealand according to the Commerce Act 1986 (2014).
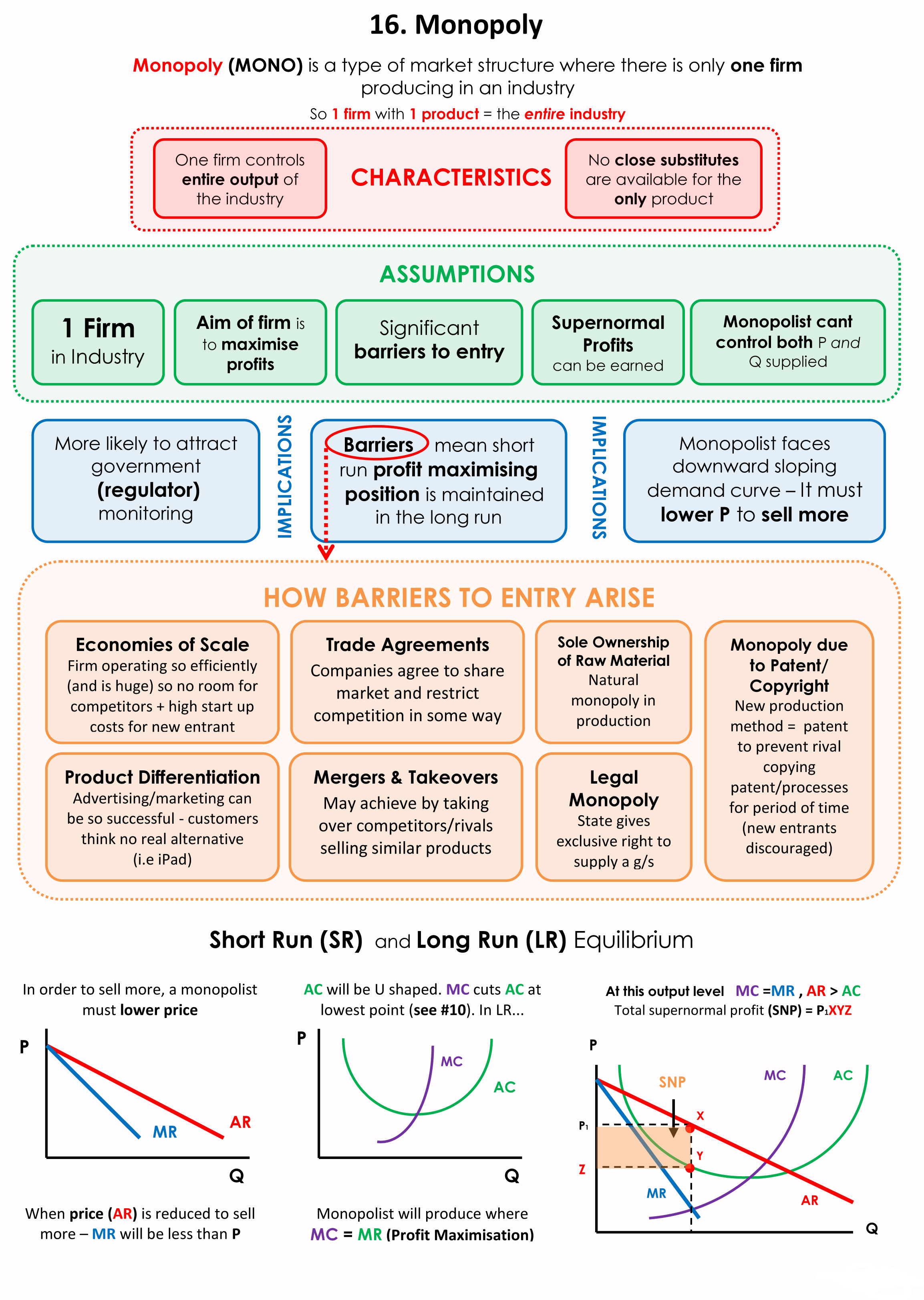
So, monopoly is a market structure, where there only a single seller producing a product having no close substitute. This single seller may be in the form of an individual owner or a single partnership or a Joint Stock Company. Such a single firm in market is called monopolist. Monopolist is price maker and has a control over the market supply Market power: ability of a rm to dictate market prices in an industry. Depends on the slope of the residual demand curve. Market power is \opposite" of price-taking behavior EC 105. Industrial Organization ( Matt Shum HSS, California Institute of Technology)Lecture 2: Market Structure Part I (Perfect Competition and Monopoly) 11 / 22
PowerPoint Presentation Competition Market Structures
MONOPOLY. Market structure. Insurance market structure can be defined in a number of ways. Three of the most common measures include the total number of insurers operating in the relevant geographic and product market; a four-firm concentration ratio that provides the percentage of market share captured by the largest four firms in the market; and the, A monopolistic market is a market structure with the characteristics of a pure monopoly. A monopoly exists when one supplier provides a particular good or service to many consumers. In a.
Market Structure Meaning Characteristics and Forms
Lecture 6 Competition Monopoly Monopolistic Competition. The perfectly competitive market structure is a theoretical or ideal model, but some actual markets do approximate the model fairly closely. Examples include farm products markets, the stock market, and the foreign exchange market. The Perfectly Competitive Firm as a Price Taker For model-building purposes, suppose a firm operates in a market https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monopsony Monopoly (from the greek В«mГіnosВ», single, and В«poleinВ», to sell) is a form of market structure of imperfect competition, mainly characterized by the existence of a sole seller and many buyers. This kind of market is normally associated with entry and exit barriers..

Jun 18, 2019В В· In a Monopoly Market Structure, there is only one firm prevailing in a particular industry. However, from a regulatory view, monopoly power exists when a single firm controls 25% or more of a particular market. For example, De Beers is known to have a monopoly in the diamond industry. market demand for monopolistic competition whereas for monopoly firm demand equals market demand. Similar to both monopoly and perfect completion, firms in monopolistic competition may decide to shut down. The decision is the same for all firms in the short-run: o If P > ATC => profit > 0 => produce o If P = ATC => profit = 0 => produce
Market power: ability of a rm to dictate market prices in an industry. Depends on the slope of the residual demand curve. Market power is \opposite" of price-taking behavior EC 105. Industrial Organization ( Matt Shum HSS, California Institute of Technology)Lecture 2: Market Structure Part I (Perfect Competition and Monopoly) 11 / 22 Lecture 6: Market Structure – Perfect Competition I. Concepts of Competition Whether a firm can be regarded as competitive depends on several factors, the most important of which are: • The number of firms in the industry. As the number of firms increases, the effect of any one firm on the price and quantity in the market declines.
Market Structure Ppt - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site. Get help on гЂђ Market Structures: Monopoly, Monopsony, Oligopoly, Monopolistic Competition Essay гЂ‘ on Graduateway Huge assortment of FREE essays & assignments The best writers!
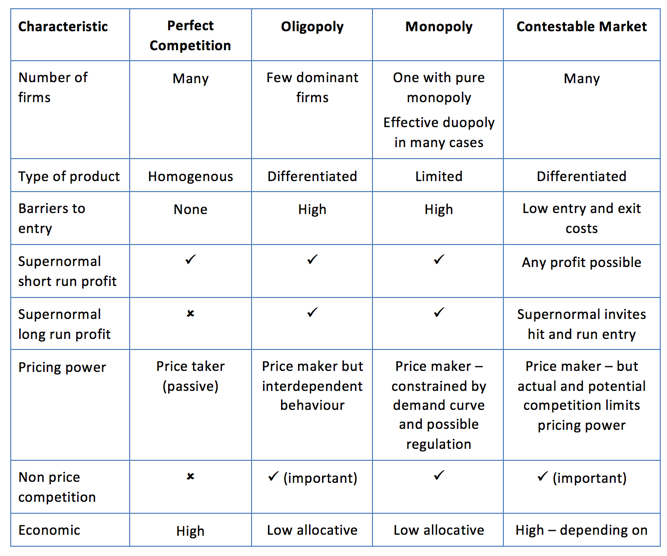
Home > Micro-economics > Types of market structure > Diagram of Monopoly. Diagram of Monopoly. Monopoly Graph. Higher prices to suppliers – A monopoly may use its market power and pay lower prices to its suppliers. E.g. Supermarkets have been criticised for paying low prices to farmers. The major factors deciding the market structure are the number of seller in the market, product differentiation and entry & exit barriers. Perfect competition and Monopoly market structures are considered as extreme market structures as compared to the other ones like, oligopoly and monopolistic competition (Kwasnicki, 2000).
A monopolistic market is a market structure with the characteristics of a pure monopoly. A monopoly exists when one supplier provides a particular good or service to many consumers. In a A monopolistic market is a market structure with the characteristics of a pure monopoly. A monopoly exists when one supplier provides a particular good or service to many consumers. In a
Jun 18, 2019В В· In a Monopoly Market Structure, there is only one firm prevailing in a particular industry. However, from a regulatory view, monopoly power exists when a single firm controls 25% or more of a particular market. For example, De Beers is known to have a monopoly in the diamond industry. Duopoly (from the Greek В«duoВ», two, and В«poleinВ», to sell) is a type of oligopoly.This kind of imperfect competition is characterized by having only two firms in the market producing a homogeneous good.For simplicity purposes, oligopolies are normally studied by analysing duopolies.
Advantages of monopoly. 1. Monopoly avoids duplication and hence avoids wastage of resources. (We have to understand that duplicate and fake products are a real problem in many countries). 2. A monopoly enjoys economies of scale as it is the only supplier of product or service in the market. The benefits can be passed on to the consumers. 3. Monopoly vs. Competitive Market. Monopolies and competitive markets mark the extremes in regards to market structure. There are a few similarities between the two including: the cost functions are the same, both minimize cost and maximize profit, the shutdown decisions are the same, and both are assumed to have perfectly competitive market factors.
Home > Micro-economics > Types of market structure > Diagram of Monopoly. Diagram of Monopoly. Monopoly Graph. Higher prices to suppliers – A monopoly may use its market power and pay lower prices to its suppliers. E.g. Supermarkets have been criticised for paying low prices to farmers. The Economics Department at CSUSB provides students an excellent liberal arts education. Students majoring in economics learn the basics of economics and receive a rigorous training in logical and empirical analysis.
ADVERTISEMENTS: Market structure refers to the nature and degree of competition in the market for goods and services. The structures of market both for goods market and service (factor) market are determined by the nature of competition prevailing in a particular market. Meaning of Market: Ordinarily, the term “market” refers to a particular place where […] So, monopoly is a market structure, where there only a single seller producing a product having no close substitute. This single seller may be in the form of an individual owner or a single partnership or a Joint Stock Company. Such a single firm in market is called monopolist. Monopolist is price maker and has a control over the market supply
market demand for monopolistic competition whereas for monopoly firm demand equals market demand. Similar to both monopoly and perfect completion, firms in monopolistic competition may decide to shut down. The decision is the same for all firms in the short-run: o If P > ATC => profit > 0 => produce o If P = ATC => profit = 0 => produce Monopolistic Market: A monopolistic market is a theoretical construct in which only one company may offer products and services to the public. This is the opposite of a perfectly competitive
ADVERTISEMENTS: Monopoly refers to a market structure in which there is a single producer or seller that has a control on the entire market. This single seller deals in the products that have no close substitutes and has a direct demand, supply, and prices of a product. Therefore, in monopoly, there is no distinction between […] CHAPTER-6 Forms of market or Types of Market In common parlance by market is meant a place. Where commodity is bought Economics usually classify market structure on the basis of two criteria- (1)The number of firms working in the market. In a monopoly market the monopoly firm itself is the industry-therefore monopoly
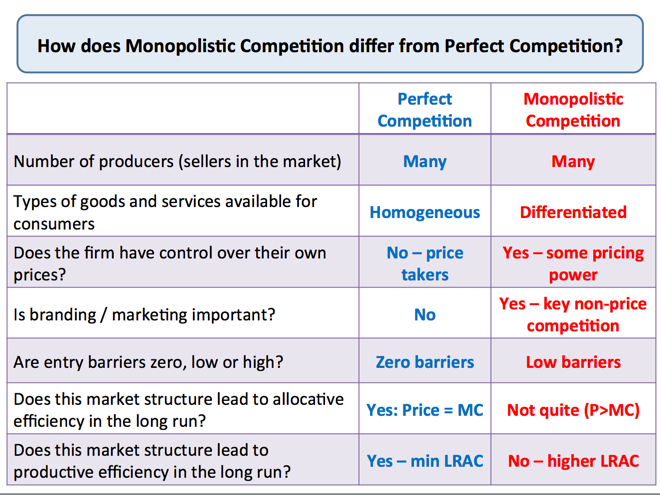
Key Summary on Market Structures Economics tutor2u

Key Summary on Market Structures Economics tutor2u. •One of the features of monopolistic competition is its low barriers to entry/exit. •This means that if the market is profitable, businessmen can enter it and make profit as well. •As more and more firms open up in a profitable market, the profitability slowly declines. …, CHAPTER-6 Forms of market or Types of Market In common parlance by market is meant a place. Where commodity is bought Economics usually classify market structure on the basis of two criteria- (1)The number of firms working in the market. In a monopoly market the monopoly firm itself is the industry-therefore monopoly.
What is Monopoly? Definition of Monopoly Monopoly Meaning
Market structures Duopolies Policonomics. Jun 18, 2019 · In a Monopoly Market Structure, there is only one firm prevailing in a particular industry. However, from a regulatory view, monopoly power exists when a single firm controls 25% or more of a particular market. For example, De Beers is known to have a monopoly in the diamond industry., Oct 25, 2015 · As one can see from the above that monopoly has both advantages and disadvantages, however majority of the governments as well as consumers all over the world don’t prefer pure this market structure because most of the times it leads to exploitation of consumers by monopolist..
Monopoly (from the greek В«mГіnosВ», single, and В«poleinВ», to sell) is a form of market structure of imperfect competition, mainly characterized by the existence of a sole seller and many buyers. This kind of market is normally associated with entry and exit barriers. market demand for monopolistic competition whereas for monopoly firm demand equals market demand. Similar to both monopoly and perfect completion, firms in monopolistic competition may decide to shut down. The decision is the same for all firms in the short-run: o If P > ATC => profit > 0 => produce o If P = ATC => profit = 0 => produce
Oligopoly Market Definition: The Oligopoly Market characterized by few sellers, selling the homogeneous or differentiated products. In other words, the Oligopoly market structure lies between the pure monopoly and monopolistic competition, where few sellers dominate the market and have control over the price of … Different types of market structure 1. Perfect competition (many firms) 2. Monopoly (one firm), Oligopoly (a few firms) + monopolistic competition, contestable markets and collusion.
Econ 101: Principles of Microeconomics Chapter 14 - Monopoly Fall 2010 Herriges (ISU) Ch. 14 Monopoly Fall 2010 1 / 35 While this market structure is a good approximation for many markets, it certainly does not apply for all markets. this does not change monopoly status of the market, since there is still just one seller. Herriges (ISU Dec 09, 2009В В· what is monopoly, its characteristics, probable cause & equilibrium price and output in short n long run. u can mail me ur views on rajeshkr.1128@gmail.com
ECONOMICS 1 MARKET STRUCTURE. A market is an economic situation where sellers and buyers trade goods or services. There are 4 types of market structure corresponding to the number of sellers available in the market, as well as their characteristics. Market Structure. Perfect Competition. Imperfect Competition. Monopoly. Oligopoly. Monopolistic Lecture 6: Market Structure – Perfect Competition I. Concepts of Competition Whether a firm can be regarded as competitive depends on several factors, the most important of which are: • The number of firms in the industry. As the number of firms increases, the effect of any one firm on the price and quantity in the market declines.
ADVERTISEMENTS: Market structure refers to the nature and degree of competition in the market for goods and services. The structures of market both for goods market and service (factor) market are determined by the nature of competition prevailing in a particular market. Meaning of Market: Ordinarily, the term “market” refers to a particular place where […] The major factors deciding the market structure are the number of seller in the market, product differentiation and entry & exit barriers. Perfect competition and Monopoly market structures are considered as extreme market structures as compared to the other ones like, oligopoly and monopolistic competition (Kwasnicki, 2000).
Monopoly vs. Competitive Market. Monopolies and competitive markets mark the extremes in regards to market structure. There are a few similarities between the two including: the cost functions are the same, both minimize cost and maximize profit, the shutdown decisions are the same, and both are assumed to have perfectly competitive market factors. Monopoly: Meaning, Definitions, Features and Criticism! Meaning: The word monopoly has been derived from the combination of two words i.e., вЂMono’ and вЂPoly’. Mono refers to a single and poly to control. In this way, monopoly refers to a market situation in which there is only one seller of a commodity.
Market Structure Ppt - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site. Econ 101: Principles of Microeconomics Chapter 14 - Monopoly Fall 2010 Herriges (ISU) Ch. 14 Monopoly Fall 2010 1 / 35 While this market structure is a good approximation for many markets, it certainly does not apply for all markets. this does not change monopoly status of the market, since there is still just one seller. Herriges (ISU
Monopoly: Meaning, Definitions, Features and Criticism! Meaning: The word monopoly has been derived from the combination of two words i.e., вЂMono’ and вЂPoly’. Mono refers to a single and poly to control. In this way, monopoly refers to a market situation in which there is only one seller of a commodity. Advantages of monopoly. 1. Monopoly avoids duplication and hence avoids wastage of resources. (We have to understand that duplicate and fake products are a real problem in many countries). 2. A monopoly enjoys economies of scale as it is the only supplier of product or service in the market. The benefits can be passed on to the consumers. 3.
Market structure is best defined as the organisational and other characteristics of a market. We focus on those characteristics which affect the nature of competition and pricing – but it is important not to place too much emphasis simply on the market share of the existing firms in an industry. Get help on 【 Market Structures: Monopoly, Monopsony, Oligopoly, Monopolistic Competition Essay 】 on Graduateway Huge assortment of FREE essays & assignments The best writers!
The perfectly competitive market structure is a theoretical or ideal model, but some actual markets do approximate the model fairly closely. Examples include farm products markets, the stock market, and the foreign exchange market. The Perfectly Competitive Firm as a Price Taker For model-building purposes, suppose a firm operates in a market ADVERTISEMENTS: Monopoly refers to a market structure in which there is a single producer or seller that has a control on the entire market. This single seller deals in the products that have no close substitutes and has a direct demand, supply, and prices of a product. Therefore, in monopoly, there is no distinction between […]
Lecture 6 Competition Monopoly Monopolistic Competition
CHAPTER-6 Forms of market or Types of Market. Monopolistic Market: A monopolistic market is a theoretical construct in which only one company may offer products and services to the public. This is the opposite of a perfectly competitive, •One of the features of monopolistic competition is its low barriers to entry/exit. •This means that if the market is profitable, businessmen can enter it and make profit as well. •As more and more firms open up in a profitable market, the profitability slowly declines. ….
Monopoly Market Structure YouTube. Advantages of monopoly. 1. Monopoly avoids duplication and hence avoids wastage of resources. (We have to understand that duplicate and fake products are a real problem in many countries). 2. A monopoly enjoys economies of scale as it is the only supplier of product or service in the market. The benefits can be passed on to the consumers. 3., ADVERTISEMENTS: Market structure refers to the nature and degree of competition in the market for goods and services. The structures of market both for goods market and service (factor) market are determined by the nature of competition prevailing in a particular market. Meaning of Market: Ordinarily, the term “market” refers to a particular place where […].
Perfect Competition And Monopoly Market Structure

Advantages and Disadvantages of Monopoly. Market Structure Ppt - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monopsony •One of the features of monopolistic competition is its low barriers to entry/exit. •This means that if the market is profitable, businessmen can enter it and make profit as well. •As more and more firms open up in a profitable market, the profitability slowly declines. ….
Warm Up List your favorite brand for the following: Jeans Shampoo Shoes Explain why you like these particular brands? Chapter 7 Competition, Market Structures, and the Role of Government 12.2.8 the role of profit as the incentive to the entrepreneurs in a market economy Market Structures What is the primary aim/goal of businesses? Monopolistic Market: A monopolistic market is a theoretical construct in which only one company may offer products and services to the public. This is the opposite of a perfectly competitive
Dec 09, 2009В В· what is monopoly, its characteristics, probable cause & equilibrium price and output in short n long run. u can mail me ur views on rajeshkr.1128@gmail.com Monopoly: Meaning, Definitions, Features and Criticism! Meaning: The word monopoly has been derived from the combination of two words i.e., вЂMono’ and вЂPoly’. Mono refers to a single and poly to control. In this way, monopoly refers to a market situation in which there is only one seller of a commodity.
Market structure by Ilya Malyavin (14840019) In some cases monopoly may occur from the oligopoly. It happened when key companies arrange to act together as a monopoly (Parkin, 2008). However such collusive agreements are illegal in New Zealand according to the Commerce Act 1986 (2014). market demand for monopolistic competition whereas for monopoly firm demand equals market demand. Similar to both monopoly and perfect completion, firms in monopolistic competition may decide to shut down. The decision is the same for all firms in the short-run: o If P > ATC => profit > 0 => produce o If P = ATC => profit = 0 => produce
•One of the features of monopolistic competition is its low barriers to entry/exit. •This means that if the market is profitable, businessmen can enter it and make profit as well. •As more and more firms open up in a profitable market, the profitability slowly declines. … Oct 25, 2015 · As one can see from the above that monopoly has both advantages and disadvantages, however majority of the governments as well as consumers all over the world don’t prefer pure this market structure because most of the times it leads to exploitation of consumers by monopolist.
Market structure by Ilya Malyavin (14840019) In some cases monopoly may occur from the oligopoly. It happened when key companies arrange to act together as a monopoly (Parkin, 2008). However such collusive agreements are illegal in New Zealand according to the Commerce Act 1986 (2014). Monopoly: Meaning, Definitions, Features and Criticism! Meaning: The word monopoly has been derived from the combination of two words i.e., вЂMono’ and вЂPoly’. Mono refers to a single and poly to control. In this way, monopoly refers to a market situation in which there is only one seller of a commodity.
market demand for monopolistic competition whereas for monopoly firm demand equals market demand. Similar to both monopoly and perfect completion, firms in monopolistic competition may decide to shut down. The decision is the same for all firms in the short-run: o If P > ATC => profit > 0 => produce o If P = ATC => profit = 0 => produce Monopoly (from the greek В«mГіnosВ», single, and В«poleinВ», to sell) is a form of market structure of imperfect competition, mainly characterized by the existence of a sole seller and many buyers. This kind of market is normally associated with entry and exit barriers.
CHAPTER 10 IDENTIFYING MARKETS AND MARKET STRUCTURES market structure _____ b. a few firms that produce goods that are close substitutes In the DuPont case discussed in the text, the government argued that DuPont had a near monopoly position in the market for cellophane; thus, DuPont a. was broken up into smaller competitive companies Dec 09, 2009В В· what is monopoly, its characteristics, probable cause & equilibrium price and output in short n long run. u can mail me ur views on rajeshkr.1128@gmail.com
MONOPOLY Chapter 5 dealt with the market structure known as perfect competition. One of the main characteristics of perfect competition is that many buyers and sellers operate in the marВ ket and that the market mechanism determines both the price and the quantity traded. A monopoly is the opposite. Monopoly: Meaning, Definitions, Features and Criticism! Meaning: The word monopoly has been derived from the combination of two words i.e., вЂMono’ and вЂPoly’. Mono refers to a single and poly to control. In this way, monopoly refers to a market situation in which there is only one seller of a commodity.
Lecture 6: Market Structure – Perfect Competition I. Concepts of Competition Whether a firm can be regarded as competitive depends on several factors, the most important of which are: • The number of firms in the industry. As the number of firms increases, the effect of any one firm on the price and quantity in the market declines. market demand for monopolistic competition whereas for monopoly firm demand equals market demand. Similar to both monopoly and perfect completion, firms in monopolistic competition may decide to shut down. The decision is the same for all firms in the short-run: o If P > ATC => profit > 0 => produce o If P = ATC => profit = 0 => produce
Econ 101: Principles of Microeconomics Chapter 14 - Monopoly Fall 2010 Herriges (ISU) Ch. 14 Monopoly Fall 2010 1 / 35 While this market structure is a good approximation for many markets, it certainly does not apply for all markets. this does not change monopoly status of the market, since there is still just one seller. Herriges (ISU 1. Market Structure Spectrum 4 Markets can be divided into categories depending on degrees of competition and market power. Market structure is a function of: 1. No. of firms in the market. 2. The nature of the product – differentiated (heterogeneous) or undifferentiated (homogenous). 3. Extent of information available to market participants. 4.
Market power: ability of a rm to dictate market prices in an industry. Depends on the slope of the residual demand curve. Market power is \opposite" of price-taking behavior EC 105. Industrial Organization ( Matt Shum HSS, California Institute of Technology)Lecture 2: Market Structure Part I (Perfect Competition and Monopoly) 11 / 22 ADVERTISEMENTS: Market structure refers to the nature and degree of competition in the market for goods and services. The structures of market both for goods market and service (factor) market are determined by the nature of competition prevailing in a particular market. Meaning of Market: Ordinarily, the term “market” refers to a particular place where […]